Innovating today for a smarter tomorrow
AI | content | teaching | learning | data | analytics
How Kortext supports higher education
Explore below how we support your role in higher ed.

Think Kortext, think:
Since 2013, we’ve been at the forefront of innovation in higher education, bringing our deep sector knowledge to everything do.
Our mission is clear: to help every student reach their full potential.
The goal may be clear, but we appreciate the complexity of achieving it.
That’s why we partner with colleges and universities across the globe, working together to enhance digital teaching, learning, and student success.
Trusted by globally respected universities
Explore the Kortext group
Discover how our cutting-edge platforms are transforming college and university education.
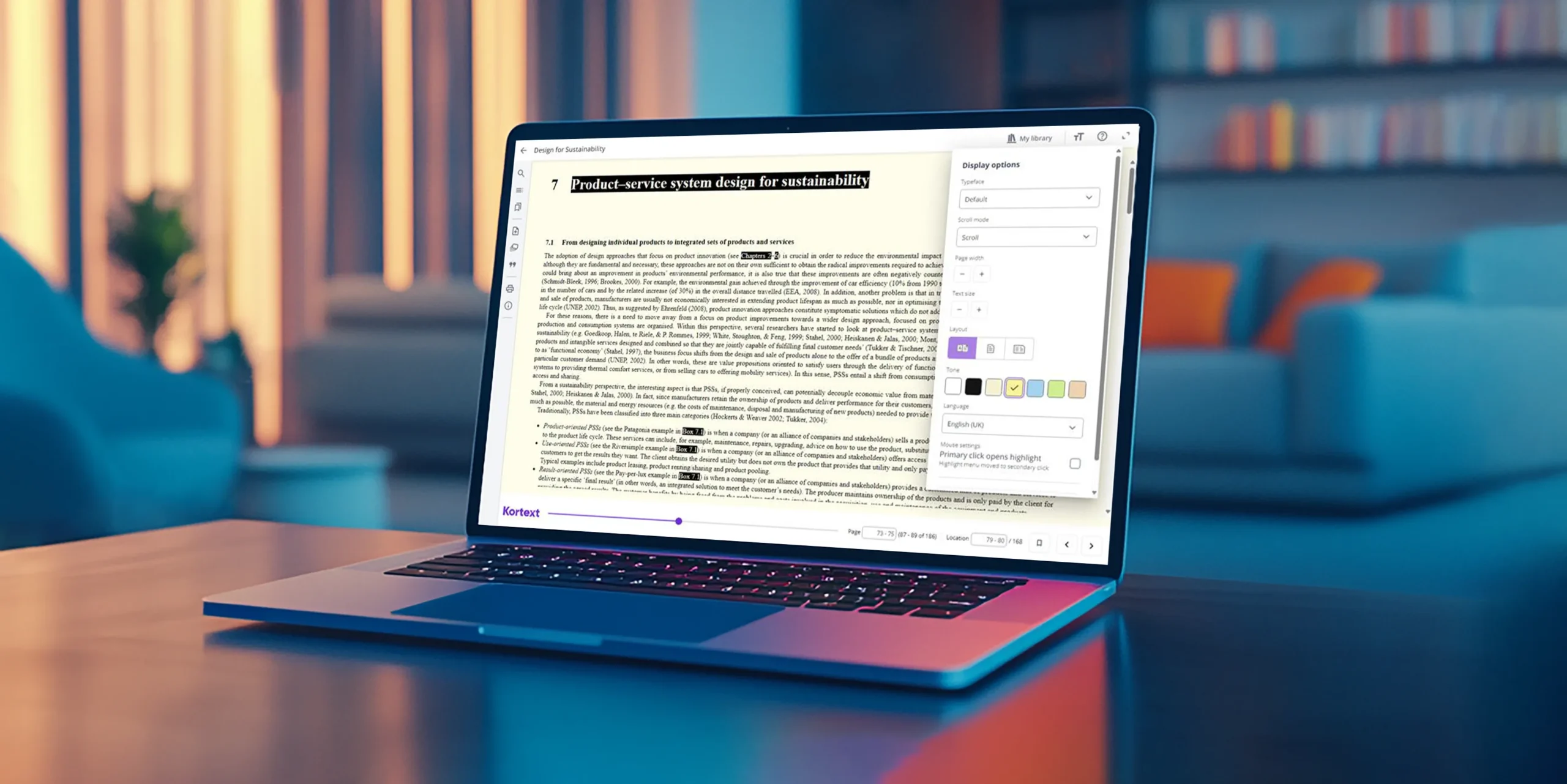
Pioneering digital education since 2013
In just over a decade, we’ve grown our offering to ten market-leading platforms serving students, faculty, librarians, publishers, and institutions.
Don’t just take our word for it—become one of over three million users optimizing their learning using Kortext.
Create a free account today and discover a new way of experiencing your content.
The power of partnership with Microsoft
At Kortext, we build upon Microsoft’s secure, reliable foundation to package their cutting-edge technologies into a suite of platforms that address the needs of every higher education stakeholder, supporting them to adapt and thrive in an emerging digital environment.

Let’s talk about what’s possible
Ready to explore further? Fill out the form today, and a member of our team will reach out to schedule a call.
We can’t wait to show you how Kortext can enhance digital teaching, learning and engagement at your institution.










